티스토리 뷰
Bitcoin 백서는 사토시 나가모토라는 가명으로 발표한 신뢰할 수 있는 제 3자 없이 온라인으로 지불이 가능한 P2P 전자 화폐인 Bitcoin을 정리한 논문이다. 요거 한번 정리해보자.
빨간색은 기존 시스템의 문제점이고 파란색은 이 논문에서 제시하고 있는 솔루션이다.
Abstract
A purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash would allow online payments to be sent directly from one party to another without going through a financial institution. Digital signatures provide part of the solution, but the main benefits are lost if a trusted third party is still required to prevent double-spending. We propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer network. The network timestamps transactions by hashing them into an ongoing chain of hash-based proof-of-work, forming a record that cannot be changed without redoing the proof-of-work. The longest chain not only serves as proof of the sequence of events witnessed, but proof that it came from the largest pool of CPU power. As long as a majority of CPU power is controlled by nodes that are not cooperating to attack the network, they'll generate the longest chain and outpace attackers. The network itself requires minimal structure. Messages are broadcast on a best effort basis, and nodes can leave and rejoin the network at will, accepting the longest proof-of-work chain as proof of what happened while they were gone
문제는 P2P 전자화폐는 온라인 Payment를 가능하게 하지만, 이중 지불을 막기 위한 제 3의 신뢰 기관이 필요하며
이 논문에서 제시하는 P2P Network를 통해 이중 지불을 해결하는 Pure P2P 전자화폐 시스템이 가능하다는 내용
Introduction
Commerce on the Internet has come to rely almost exclusively on financial institutions serving as trusted third parties to process electronic payments. While the system works well enough for most transactions, it still suffers from the inherent weaknesses of the trust based model. Completely non-reversible transactions are not really possible, since financial institutions cannot avoid mediating disputes.
전자 상거래의 Payment의 경우 신뢰할 수 있는 제 3자 역할의 금융기관에 의존하고 잘 동작하고 있지만 문제점이 있다.
금융 기관들은 분쟁 조정을 피할수 없으므로 완전히 취소 불가능한 거래는 사실상 불가능하다.
The cost of mediation increases ① transaction costs, limiting the minimum practical transaction size and cutting off the possibility for small casual transactions, and ② there is a broader cost in the loss of ability to make non-reversible payments for nonreversible services. With the possibility of reversal, the need for trust spreads. Merchants must be wary of their customers, hassling them for more information than they would otherwise need.
조정 비용으로 인해 발생할 수 있는 문제
① 거래 비용의 증가, 최소한의 실용적 트랜잭션 크기를 제한하고 최소 일상 거래의 가능성을 차단해야 하기 때문
② 환불과 같은 취소 규정이 없는 서비스를 실제 취소 불가능하게 만들기 위한 비용이 더 많이 듦
즉 ,100원과 같은 소규모 거래들 분쟁까지 조정할 수 없으므로 트랜잭션을 제한함으로써 비용이 증가한다는 말이다. 거래 취소 가능성으로 더 큰 수준의 신뢰수준이 필요하며 판매자는 소비자들에게 주민등록번호와 같은 필요하지 않았을 귀찮은 정보들을 요구할 수 밖에 없다는 것이다.
A certain percentage of fraud is accepted as unavoidable. These costs and payment uncertainties can be avoided in person by using physical currency, but no mechanism exists to make payments over a communications channel without a trusted party.
일정 수준의 사기는 불가피하다. 이런 불확실성은 실제 화폐를 직접 사용함으로써 피할 수 있지만, 제 3의 신뢰기관 없이 이런 communication channel을 통해 Payment를 할 수 있는 메커니즘은 없다.
위 내용을 요약해보면, 실생활의 온라인 거래는 금융기관 같은 제 3의 신뢰기관을 통해 하고 이로 인해 거래 조정을 위한 불필요한 제약과 비용이 들며 사용자들만 불편해 지는 것이다.
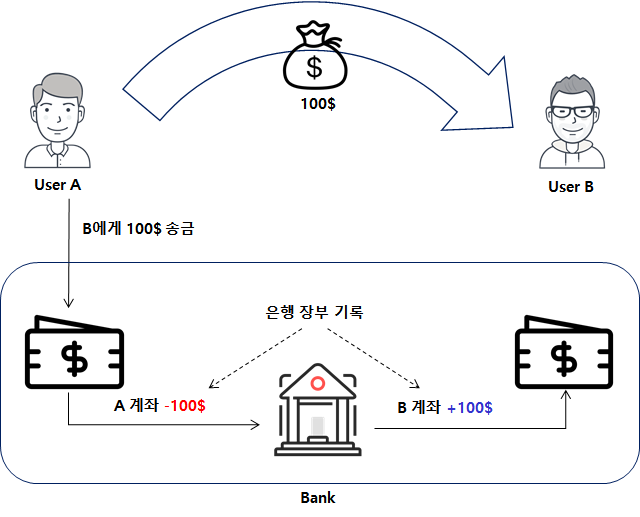
위 그림과 같이 기존의 전자 상거래를 보면 A는 B에게 온라인을 통한 송금 거래를 할 때 은행이라는 금융기관을 통해서 요청을 하고 실제로는 A 계좌의 돈을 차감, B 계좌의 돈을 증액 시키는 기록상의 변경이 일어난다. 하지만, 이 온라인 Payment에 대한 프로세스는 제 3의 기관을 통해서만 가능하다는 것이다.
결국, 제 3의 기관 없이 온라인 상의 거래를 신뢰성 있게 하고 싶은게 궁극적인 목표이다. 제 3의 기관에게 전적으로 의존하게 된다면 위와 같은 문제도 있고 Single Point of Failure 문제도 발생하게 되는데 은행과 같은 신뢰기관이 파산되거나 사기를 친다면 누구를 탓할 수 없다.
What is needed is an electronic payment system based on cryptographic proof instead of trust, allowing any two willing parties to transact directly with each other without the need for a trusted third party. Transactions that are computationally impractical to reverse would protect sellers from fraud, and routine *escrow mechanisms could easily be implemented to protect buyers
필요한 것은 신뢰 대신 암호학적 증명 기반의 전자상 거래 시스템이며 이는 제 3자 없이 서로간의 직접 거래를 가능하게 해준다. 이 시스템의 계산적으로 취소가 불가능한 거래는 판매자들을 사기로부터 보호해준다. 구매자를 보호해주는 *escrow 메커니즘은 쉽게 구현될 수 있다.
※ escrow : 흔히 안전거래 시스템과 같이 제 3자가 개입하여 구매자의 지불한 금액을 판매자로부터 거래 물품을 받았음을 확인할 때 넘겨주는 서비스를 말한다.
In this paper, we propose a solution to the double-spending problem using a peer-to-peer distributed timestamp server to generate computational proof of the chronological order of transactions. The system is secure as long as honest nodes collectively control more CPU power than any cooperating group of attacker nodes.
이 논문에서는 거래의 시간적인 순서의 계산적 증명을 생성하기 위한 P2P 분산 Timestamp 서버를 사용해 이중 지불 문제를 해결할 솔루션을 제시한다. 이 시스템은 정직한 노드들의 컴퓨팅 파워 합이 공격자 노드들의 연합보다 크면 안전하다.
서론을 정리하자면, 제 3의 기관 없이 전자 상거래를 위해서는 이중 지불과 같은 문제가 없다는 신뢰성이 필요한데 이 논문에서 제시하는 솔루션으로 해결할 수 있다고 한다.
시간적인 순서의 계산적 증명을 생성하기 위한 P2P 분산 Timestamp 서버에서 사용되는 개념들을 아래에서 소개한다.
Reference
https://www.bitcoin.com/get-started/bitcoin-white-paper-beginner-guide/
'Architecture > Financial' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [해외송금] SWIFT 거래와 리플 (4) | 2021.07.23 |
|---|---|
| [블록체인] 카르다노 (ADA) 백서 정리 #2 - 메커니즘 (0) | 2021.06.23 |
| [블록체인] 카르다노 (ADA) 백서 정리 #1 - 동기 (0) | 2021.06.22 |
| [블록체인] Bitcoin 백서 정리 #3 - 정리 (1) | 2021.06.04 |
| [블록체인] Bitcoin 백서 정리 #2 - 메커니즘 (0) | 2021.06.04 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- 카르다노
- 암호화폐
- Nealford
- Bitcoin
- 비트코인
- Java
- 사토시 나가모토
- Spring
- architecture
- Redis
- gRPC
- 동적계획법
- vuejs
- 아키텍처
- excel parsing
- SpringBoot
- 블록체인
- 알고리즘
- 스프링 시큐리티
- white paper
- kubernetes
- leetcode
- 백준
- Vue.js
- CARDANO
- Bruteforce
- DP
- 스프링
- Blockchain
- k8s
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 |
| 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 |
| 28 | 29 | 30 |
